 All modules address a specific Next Generation Science Standard (NGSS) performance expectation, as well as allow students to experience the process of science.
All modules address a specific Next Generation Science Standard (NGSS) performance expectation, as well as allow students to experience the process of science.
General Elements of 2nd - 8th Grade Modules:
- Observe a Phenomenon or Set of Phenomena
- Identify Variables
- Design an Experiment, Select Variables
- Carry Out Experiment
- Analyze Data and Draw Conclusions
- Present Results in a Poster and Present
All Modules are NGSS-Aligned for each grade level.
| 2nd Grade | 6th Grade |
| 3rd Grade | 7th Grade |
| 4th Grade | 8th Grade |
| 5th Grade | 9th- 12th Grade |
| SciTrek-Inspired Lessons by Classroom Teachers |
Jump to Secondary Modules (7-8 Grade)
 |
Module 1: Soil Water Retention In the Soil Water Retention Module students learn about what variables affect the amount of water a soil can absorb. They explore variables such as soil compactness, liquid amount, liquid thickness, soil amount and soil type. Students relate their findings back to landslides and then look at how engineers design solutions to prevent landslides. (2-ESS2-1) |
|
Module 2: Plants In the Plants Module students grow "fast plants" and learn about what variables affect plant growth. They explore variables such as soil type, liquid amount, nutrient type, and light amount. In this module students work on graphing skills. (2-LS2-1) |
 |
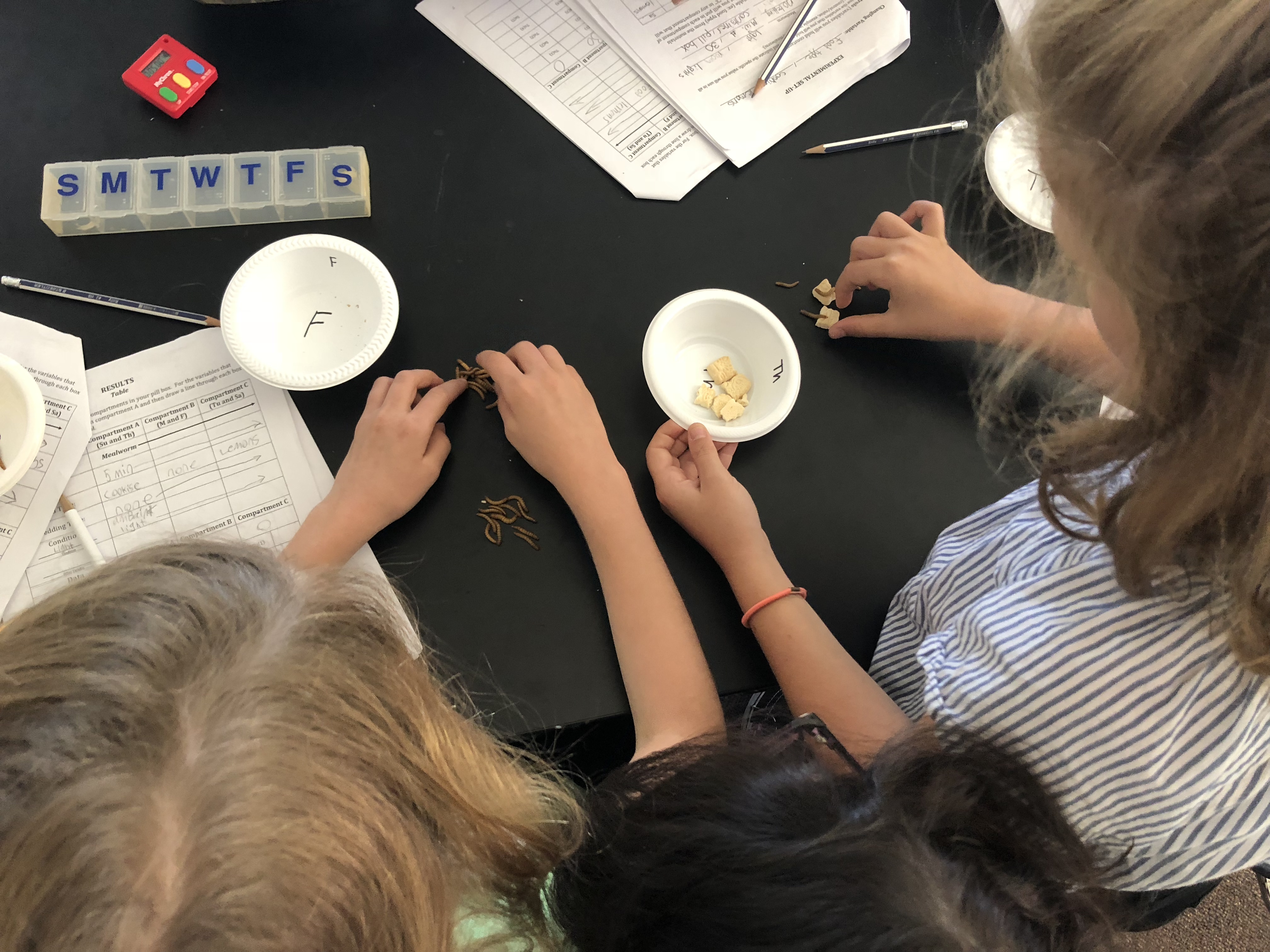 |
Module 1: Mealworms In the Mealworms Module students learn about mealworms habitats. Students explore variables such as moisture level, food type, bedding, and light amount to determine which direction mealworms travel. Once they learn about a mealworms habitat the explore what happens to a species when their habitat changes. (3-LS4-3). |
|
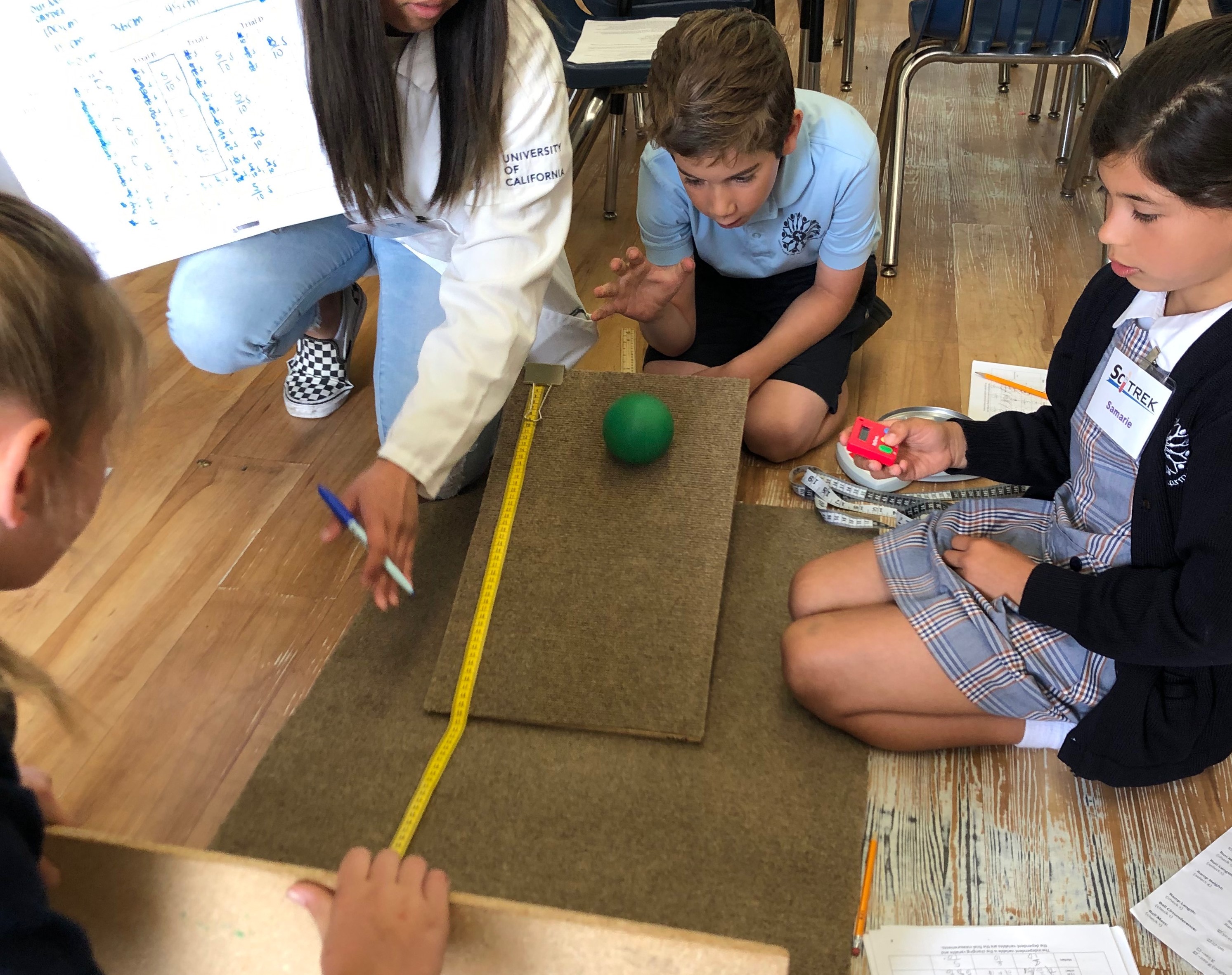
Module 2: Motion In the Motion Module students role balls down ramps and learn about what variables affect ball motion. They explore variables such as run material, ball mass, ball circumference, ramp length, run length, and ramp height. They use these studies to predict ball motion. In this module students work with fractions. (3-PS2-2) |
 |
 |
Module 1: Respiration In the Respiration Module students are given bottles with blue solution in which they can change the contents and conditions of the bottles. When the bottles sit for 24 hours some of the bottles change to yellow. Students explore what makes the bottles change color. Students explore variables such as aquatic animal type, plant type, and light amount. The results of their finding show that the presence of CO2 is the cause of the color change. They use this to learn about respiration in plants and animals as well as photosynthesis. In addition they explore how CO2 levels are changing in the environment. (4-LS1-1). |
|
Module 2: Wind Turbines In the Wind Turbine Module students explore how changing a wind turbine affect the amount of current the wind turbine produces. They explore variables such as blade materials, blade angle, turbine angle, amount of weights, run material, ball mass, and number of blades. They use the class results to engineer the wind turbine the produces the most current. In addition students explore types of energy and how energy is transferred. (4-PS3-4) |
|
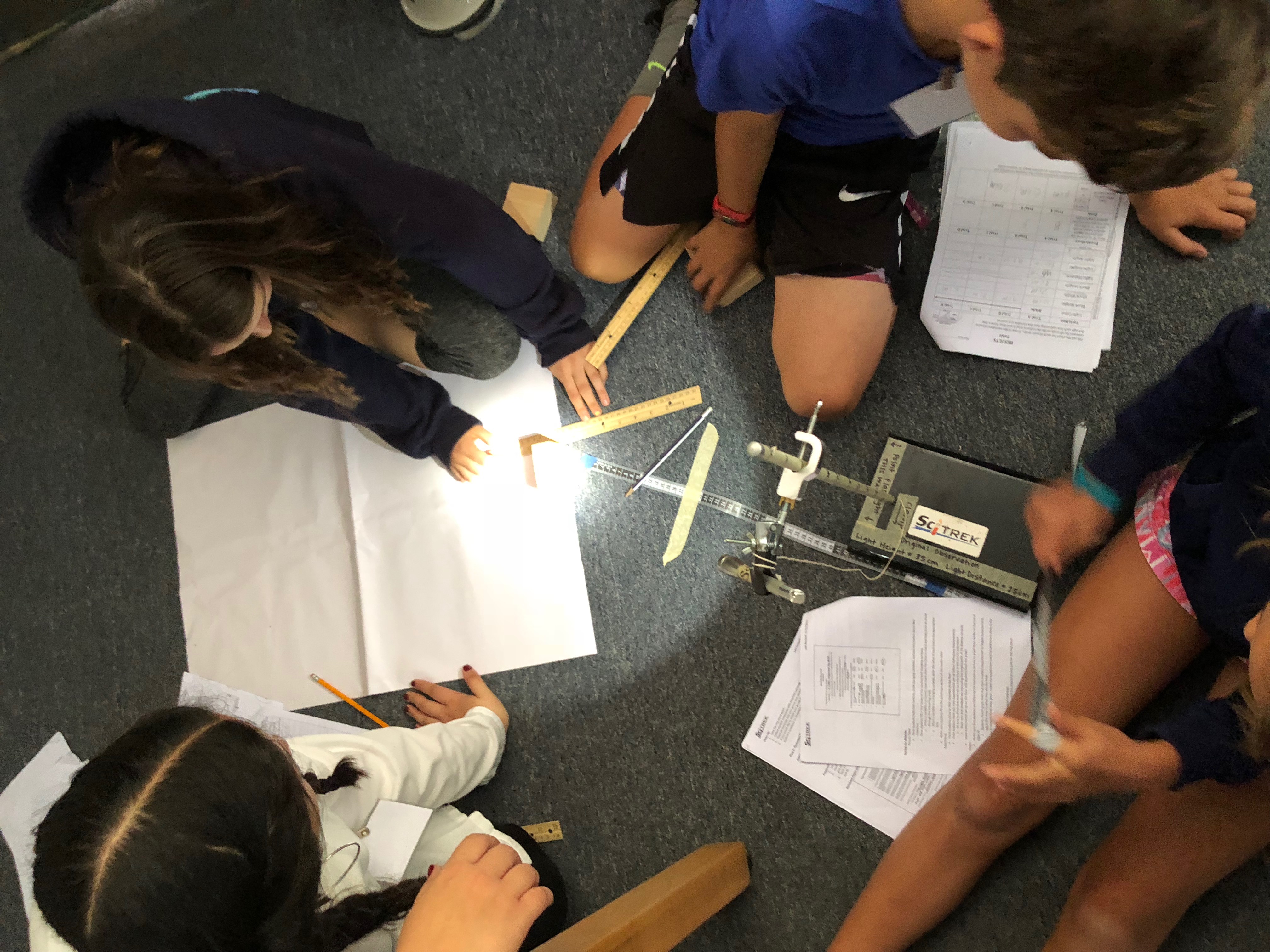 |
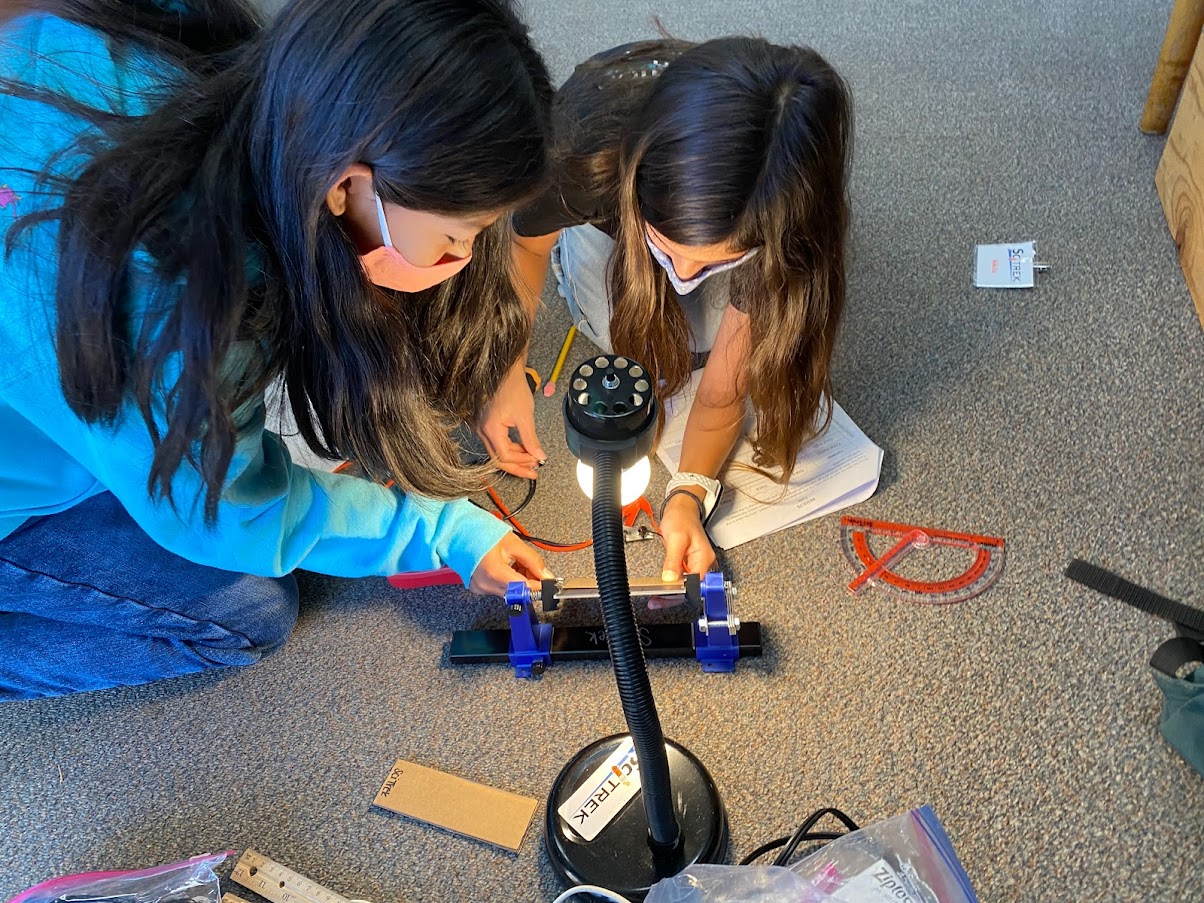
Module 1: Shadows In the Shadows Module students learn about shadows length and width. They explore variables such as light color, light height, light distance, object height, object length, and object width. They then apply these finding to predicting the shadows the sun make both in the winter and in the summer. (5-ESS1-2) |
|
Module 2: Chromatography In the Chromatography Module, students learn about smears produced by pens. They explore variables such as pen type, pen color, liquid type, and initial dot height. They apply these findings to further understand matter and physical properties. Then, they are able to use types of physical properties to identify different substances. (5-PS1-3) |
 |
 |
Module 1: Solar Power In the Solar Power Module, students learn about the amount of power that a solar panel can produce. They explore variables such as panel angle, temperature, and shading affects. They apply these findings to think about power sources and their effects on teh environment as well as ways to minimize our power consumption specifically when using light bulbs. They learn how to work in teams to plan their investigations to obtain data from their experiments that will allow them to make further predictions about the power produced by a solar panel at any configuration of the three variables. (MS-ESS3-3).
|
|
Module 2: Thermal Transfer
In the Thermal Transfer Module, students learn how mixing four different substances affects the temperature change during a chemical reaction. They explore variables such as calcium chloride mass, sodium chloride mass, sodium bicarbonate mass, water volume, and stirring speed. They also learn that if they work as a class instead of individual group they get more usable information from the experiments and they are able to predict the temperature change regardless of the amount of the substance that are combined. (MS-PS3-4)
|
 |
Secondary Modules
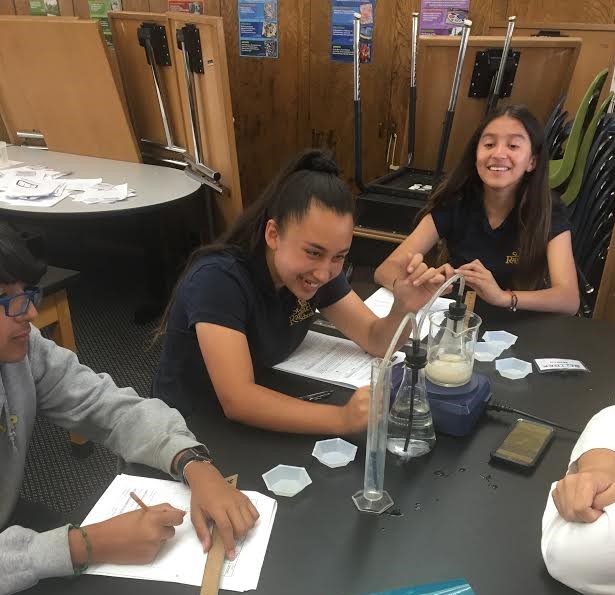 |
Module 1: Best Bread In the Best Bread module, students observe cellular respiration using a common household microorganism, yeast. Students investigate how to optimize yeast growth using a specific protocol of collecting CO2. This module focuses on the best way to create the conditions where yeast grows at various rates and generates varying amounts of CO2 using these specific variables. The final activity is a challenge engineering activity, where students work in groups try to get their yeast to create the most CO2. |
|
Module 2: Conservation of Mass In the Conservation of Mass module, students will explore how chemical reactions affect mass by performing several different types of reactions. Near the end of the module, the students are tasked with an engineering problem where they need to create a closed system to contain all the gas created in the final reaction. The main goal is to have the students realize that gasses, either as reactants or products, should be considered when they are evaluating whether the total mass is conserved. The students are guided in a discussion about open and closed systems and how gasses must be included when considering conservation of mass. |
|
 |
Module 1: Waves In the Waves module, students learn how waves are mechanical phenomena that, in the case of sound waves, move through a medium. Students have the opportunity to observe how different media can either amplify or dampen waves, and why. Students will be able to manipulate an environment to achieve the goal of amplifying or nullifing sound. The final activity in this Module is a challenge engineering activity where students build an environment that allows sound to travel the best. |
|
Module 2: Germs In the Germs module, students explore how specific bacteria, just like anyone, thrive only in a specific environment. Students can manipulate the environment of these organisms to see how the variables they introduce affect bacterial growth. Students get real wetlab experience as they practice, together with their undergraduate SciTrek Mentor, har how to plate organisms on agar to observe differences in growth. |
|
Our High School Modules are currently under construction. Check back in 2025 for updates!
SciTrek-Inspired Lessons by Classroom Teachers
1st Grade
- Tin Can Phones: for more information, please contact Tanya Juarez at tanya.juarez@venturausd.org
4th Grade
- Stomp Rockets: for more information, please contact Lauri Dahlin at lauri.dahlin@peabodycharter.net
